What is Cat 7 Cable?
5/8/2023 10:51:18 AM
Ⅰ Introduction of Cat 7 cable
Cat 7 cable is an 8-core shielded cable. Each pair of them has a shield (generally Foil Shield). There is a shield (generally Braided Shield) outside the 8 cores with the same interface as RJ-45. The maximum transmission frequency of Category 7 cable S/FTP Cat.7 (HSYVP-7) is 600MHz, and the transmission frequency of Super Category 7 cable is 1000MHz.
Cat 7 Ethernet cable is no longer an unshielded twisted pair, but a shielded twisted pair, so it can provide a combined attenuation to crosstalk ratio of at least 500MHZ and an overall bandwidth of 600MHZ, which is more than twice that of Category 6 and Cat6e cable, with transmission rates up to 10Gbps.
There are many significant differences between Cat 6 and Cat 7 cabling systems, and the most obvious being bandwidth. Cat 6 channels offer a combined attenuation to crosstalk ratio of at least 200 MHZ and an overall bandwidth of 250 MHZ. Cat 7 systems can provide a combined attenuation to crosstalk ratio of at least 500 MHZ and an overall bandwidth of 600 MHZ.
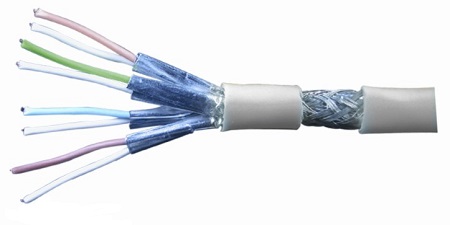
CAT 7 cable
A large number of broadband applications drive the need for more bandwidth. For example, a typical Cat 7 channel can provide a bandwidth of 862 MHZ on one pair of wires to carry video signals. Analog audio signals are transmitted in another pair, and then high-speed LAN information is transmitted in the third and fourth pairs.
Another difference between Cat 6 and Cat 7 systems is their structure. Cat 6 cabling systems can use both UTP and STP, while Cat 7 systems are based on shielded cables only. In Cat 7 cable, each pair of wires has a shield, and four pairs of wires together have a common large shield. Physically, the additional shield allows Cat 7 cables to have a larger wire diameter.
Another important difference is the capability of the connection hardware. The parameters of the Cat 7 system require the connectors to provide at least 60DB of combined near-end stringing for all pairs at 600MHZ. While the Cat5e system only requires 43dB to be provided at 100MHZ, the value for Cat 6 at 250MHZ is 46dB.
Ⅱ Reasons for Proposal of Cat 7 cable
Cat 7 cable is proposed based on the following reasons.
1. Compared with fiber optic LAN, the solution of the Cat 7 system provides the desired performance and bandwidth, but its overall cost is only a fraction of fiber optic.
2. Fiber-optic systems can provide enough bandwidth and fiber optic cables are close in price to Cat 7 cables. However, the price advantage of fiber is quickly lost when the cost of fiber routers, optical switches, and optical network cards is factored in.
However, before Cat 7 cable had a chance to demonstrate its true advantages in both of these areas, the cost of optical communication networks was already greatly reduced. Because of the natural advantages of optical communication in terms of transmission distance, Cat 6 cable was comprehensively suppressed by optical communication before it had a chance to grow rapidly.
Ⅲ Types of Ethernet cables
The general household is "Super Category 5", the following is a detailed description.
(1) Cat 1 cable: The highest frequency bandwidth of the cable is 750kHZ, which is used for alarm systems, or only for voice transmission and is different from data transmission.
(2) Cat 2 cable: Its maximum frequency bandwidth is 1MHZ, used for voice transmission and the highest transmission rate of 4Mbps data transmission, commonly used in the old token network using the 4MBPS specification token transfer protocol.
(3) Cat 3 cable: It refers to the cable specified in the ANSI and EIA/TIA568 standards. The cable's transmission frequency is 16MHz. The maximum transmission rate is 10Mbps (10Mbit/s), mainly used for voice. 10Mbit/s Ethernet (10BASE-T) and 4Mbit/s token ring: the maximum length of the network segment is 100m. Using RJ form of the connector, it has faded out of the market.
(4) Cat 4 cable: This type of cable has a transmission frequency of 20MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission at a maximum transmission rate of 16Mbps (referring to 16Mbit/s token ring), and is mainly used for token-based LAN and 10BASE-T/100BASE-T. The maximum segment length is 100m, with RJ-type connectors, and has not been widely adopted.
(5) Cat 5 cable: This type of Cat 5 cable has increased winding density, coats a high-quality insulation material. The cable's maximum frequency bandwidth is 100MHz, and the maximum transmission rate is 100Mbps. It is used for voice transmission and has the highest transmission rate of 100Mbps data transmission, mainly for 100BASE-T. The maximum network segment length of 100m. Using the RJ form of the connector, it is the most commonly used Ethernet cable. Within the twisted pair cable, different pairs have different strand lengths. Usually, four pairs of twisted wire twist cycle within 38.1mm length, twisted in a counterclockwise direction, the twisted length of a pair is within 12.7mm.
(6) CAT5e cable: CAT5e cable has advantages of small attenuation, less crosstalk, and it has a higher attenuation to crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (Structural Return Loss), smaller time delay. CAT5e cables are mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps).
(7) Cat 6 cable: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz to 250MHz. Cat 6 cabling system has a larger margin of integrated attenuation crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) at 200MHz, which provides 2 times the bandwidth of CAT5e. The transmission performance of Cat 6 cabling is much higher than the CAT5e standard and is most suitable for applications with transmission rates higher than 1 Gbps. An important difference between Cat 6 and CAT5e is the improved performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss, which is extremely important for the new generation of full-duplex, high-speed network applications. The Cat 6 standard eliminates the basic link model, and the cabling standard uses a star topology, requiring a cabling distance of no more than 90m for a permanent link and 100m for a channel.
(8) CAT6e: CAT6e cable is an improved version of Cat 6 cable, which is also an unshielded twisted pair cable specified in ANSI/EIA/TIA-568B.2 and ISO Class 6/E standards, and is mainly used in gigabit networks. In terms of transmission frequency, it is the same as Cat 6 cable, also 200 to 250 MHz, and the maximum transmission speed can also reach 1000 Mbps. Another feature is the addition of a cross-shaped pair separator between the four twisted pairs. Without the cross divider, one pair of cables in the cable may get trapped in the gap between the two cables of the other pair, reducing the spacing between the pairs and aggravating crosstalk problems. The divider also works with the outer jacket of the cable to hold the four pairs of cables tightly in their designed positions and can reduce the bending of the cable to bring about the loosening of the pairs, thus reducing the degradation of performance during installation.
(9) Cat 7 cable: This cable is the latest type of twisted pair in the ISO Cat 7 / Class F standard, which is mainly designed to accommodate the application and development of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology. But it is no longer an unshielded twisted pair, but a shielded twisted pair, so it can provide at least 500MHZ of combined attenuation to crosstalk ratio and 600MHZ of overall bandwidth, which is more than two times that of Cat 6 and CAT6e, with transmission rates up to 10Gbps.
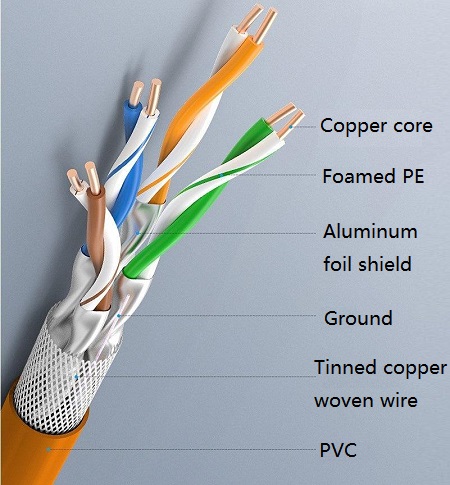
CAT 7 cable composition
(10) Cat 8 cable: Internationally, only Cat 7 cables are defined, but Siemon in the US has announced the development of Cat 8 cables, which were developed by the company in 1999 under the trademark "Tera" and are also known as "tera", "tera dor", "10Gip" and "megaline 8". The Cat 8 cable is also known as "tera", "tera dor", "10Gip" and "megaline 8". The Cat 8 network has a bandwidth of 1200MHz, allowing it to provide multiple services simultaneously, handling Terrestrial TV, CCTV, DAB, FM, audio, IR control, 10/100 and 100/1000 Ethernet, video, telephony, USB peripherals, and more.
Ⅳ Advantages of Cat 7 cable
Rapidly evolving network applications have led to increasing demand for bandwidth, and the June 2002 ANSI/TIA/EIA568-B copper twisted pair Cat 6 standard meets most commercial applications with its 250MHz bandwidth. However, as technology continues to advance, the 250MHz bandwidth cannot adequately meet the needs of people.
The choice of cable type should be considered from a variety of aspects such as cable usage, required transmission capacity, transmission bandwidth, and price. Cable types are unshielded twisted pair, shielded twisted pair, and fiber optic cable.
As early as 1997, cabling standardization bodies and manufacturers have proposed the idea of a Cat 7 copper cabling system. It provides a combined attenuation to crosstalk ratio of at least 500MHz and an overall bandwidth of 600MHz, with connectors that require all pairs to provide at least 60dB of combined near-end crosstalk at 600MHz.
Recommended News
-
Tel
0755-23616330 -
Whatsapp

 English
English
 English
English 简体中文
简体中文 Russia
Russia
 2023-05-08
2023-05-08

![A Guide to AVR Microcontroller [PDF] A Guide to AVR Microcontroller [PDF]](/upload/202306/03/202306031435158708.jpg)